When To Seek Medical Care
Its important to consult with a physician if you experience digestive symptoms that persist for more than two weeks. Even if you dont have noticeable celiac disease symptoms, you may want to get tested if someone in your family has this condition. Its also imperative to speak with a medical professional before trying out a gluten-free diet.
Celiac Disease Or Wheat Allergy
These are different pathologies.Unlike celiac disease, wheat allergy can be triggered not only in the intestinal area but also affect, for example, airways and skin, as well as lead to anaphylactic shock in the most serious cases.
Furthermore, in the case of wheat allergy, the consumption of wheat alone should be avoided, while there are many cereals that contain gluten, including: oats, barley, rye, spelled, kamut.
In any case, to facilitate a differentiated diagnosis, tests can be performed to identify wheat allergy through the presence or absence of some IgE class antibodies and PRICK tests.
How To Manage Symptoms Of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a lifelong condition that has no cure. However, people with this condition can manage their symptoms effectively by adhering to a strict gluten-free diet.
This means that you must avoid any products containing wheat, barley, rye, or spelt, including any foods that may have been cross-contaminated, such as oats, unless theyre labeled as gluten-free.
Recommended Reading: Domino’s Gluten Free Pizza Ingredients
Diagnosis Of Celiac Disease
Diagnosis of celiac disease is made through blood tests and duodenal biopsy. Obviously, these investigations must absolutely be carried out when the patient is on a free diet, i.e. including gluten.
Blood tests
Blood tests that allow to determine level of antibodies produced by the immune system in the event that gluten is perceived as a harmful substance:
- anti-transglutaminase
- anti-endomysium and anti-gliadin , to replace and / or complement the anti-transglutaminase.
Intestinal biopsy
If the blood sample gives a positive result, a biopsy of the duodenum is usually also performed, during esophagus-gastro-duodenoscopy, to evaluate the state of the intestinal villi .
According to the most recent guidelines, biopsy can be avoided in children and adolescents in the presence of elevated antibody values and symptoms typical of the disease.
Genetic test
When the dosage of antibodies, duodenal biopsy and symptomatological picture do not give clear results, the genetic test is used. This procedure detects whether one is predisposed to the disease through the presence of the HLA-DQ2 and HLA DQ8 genes.
Being positive on the genetic test does not mean that you are celiac, but it does mean that you are more likely to develop celiac disease than the general population. A negative genetic test, on the other hand, makes it highly unlikely that the patient will develop celiac disease.
You Have An Autoimmune Disease

An autoimmune disease is the term given when your immune system mistakenly attacks and damages your own tissue.
There are more than 80 types, characterised by which tissues or organs in the body are damaged.
Gluten intake is consistently linked with numerous types, but whether its the cause remains to be seen. Its influence in Celiac disease is the obvious example, but research indicates gluten likely affects Hashimotos hypothyroidism and Graves disease, to name a few.
Some researchers speculate the potentially negative effect of gluten is to do with the effect that gliadin may have on gut health and function .
In any case, it seems gluten intolerance is more likely in those with an autoimmune condition.
Recommended Reading: Gluten Dairy Sugar Free Diet
When Should I Call My Doctor
Some symptoms of gluten exposure can be severe. Seek medical attention if you experience diarrhea or vomiting. Dehydration can lead to dangerous electrolyte imbalances.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Gluten intolerance may make you feel sick after eating gluten. You might get bloated, nauseous or gassy. Gluten intolerance causes a lot of the same symptoms as celiac disease, but its not the same condition. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that leads to damage to the digestive tract. People with gluten intolerance usually find relief from their symptoms by following a gluten-free diet. Gluten-free diets do have some health risks. Its important to work with your healthcare provider and a dietitian to build the right treatment plan for your needs.
Could Your Symptoms Be The Result Of A Wheat Allergy
If youve been tested for celiac and the results were negative, theres a chance you simply have an allergy to wheat.
- Nausea and gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea or vomiting
- Asthma
- Anaphylaxis
These symptoms may appear after you eat foods with wheat, including bread, cereal, or granola. Because these foods also contain gluten, a wheat allergy is commonly called a gluten allergy, though theres actually no such thing.
Also Check: Snyder’s Of Hanover Gluten Free Pretzel Sticks
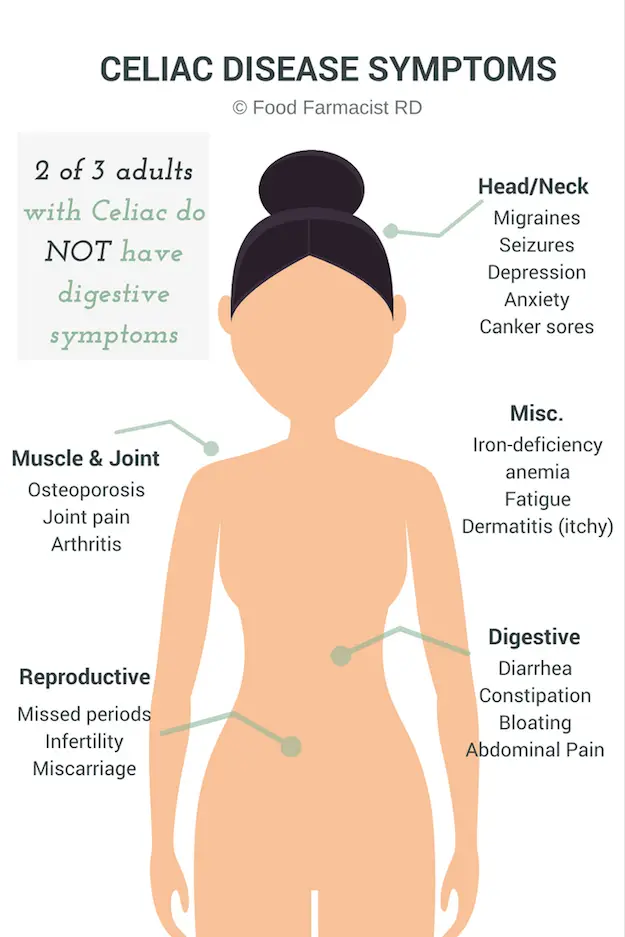
Common Symptoms Of Celiac Disease
If you have celiac disease, diagnosis may take time because the symptoms that people think ofâdiarrhea, weight loss, and bloatingâare just part of the picture. Some people with celiac disease may exhibit other nondigestive symptoms, or sometimes people have no symptoms at all.3
Symptoms in Adults
More than half of adults with celiac disease have signs and symptoms that are not related to the digestive system, including:
- Itchy, blistery skin rash
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Loss of bone density
- Damage to dental enamel
Infants and children tend to experience digestive problems such as:
- Abdominal bloating and pain
- Vomiting
- Constipation
Children can also experience other nondigestive symptoms, including fatigue, irritability, behavioral issues, delayed growth and puberty, and failure to thrive.2,5
Actions For This Page
- Coeliac disease is an autoimmune disease where the immune system reacts abnormally to gluten.
- For people with coeliac disease, even small amounts of gluten can damage the lining of the small intestine , which prevents the proper absorption of food nutrients. Inflammation also occurs elsewhere in the body.
- If you have coeliac disease, inflammation and damage can occur even if you have no symptoms.
- Correct diagnosis of coeliac disease in adults can only be made by gastroscopy.
- There is no cure, but coeliac disease can be managed by a lifelong gluten-free diet.
- A person with coeliac disease can still have a nutritious, balanced and varied diet.
Read Also: Gluten Free Sugar Cookie Recipe
How Common Is Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is now recognized as one of the most common chronic diseases in the world. It is estimated that it affects as many as 1 in every 100 – 200 people in North America. As many as 300,000 Canadians could have this disease however, many remain undiagnosed.
First-degree relatives of a person with celiac disease have about a 10% chance of having this condition. Therefore, family members, especially if they have symptoms, should be tested for celiac disease. Testing for celiac disease is also recommended for individuals with Type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease and Down syndrome since they too have a higher risk of having celiac disease.
Are There Supplements That Are Good For People With Celiac Disease
- Iron
- Copper
A multivitamin or nutritional supplement can help you rebuild your levels of essential nutrients.
But keep in mind that some vitamins, minerals, and herbal supplements may contain gluten. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking any nutritional supplement to make sure it doesn’t contain gluten.
Recommended Reading: Gluten Free Dairy Free Frozen Meals
How Is Celiac Disease Diagnosed
Celiac disease can be hard to diagnose. Its symptoms may look like symptoms of other digestive problems such as:
-
Crohn’s disease
-
Intestinal infections
-
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
To see if you have celiac disease, your healthcare provider will look at your past health and do a physical exam. You may also have tests such as:
-
Blood work. This is done to check the level of infection-fighting cells you have to gluten in your blood. People with celiac disease have higher than normal levels of these cells. Your immune system makes these cells to help fight things that the body feels are a danger.
-
Biopsy. This is the most accurate way to tell if you have celiac disease. A tissue sample is taken from your small intestine to check for damage to the villi. To do this, a long, thin tube is placed in your mouth, down to your stomach and into your small intestine. A tissue sample is taken using tools passed through the tube. The sample is checked in a lab.
Celiac Disease Tests And Diagnosis
Doctors use blood tests and other tests to help find out if you have celiac disease:
- Serology tests look for certain antibodies.
- Blood tests check other parts of your immune system.
- Intestinal fatty acid binding protein tests show if thereâs damage to the intestine.
- A complete blood count looks for anemia .
- C-reactive protein tests show if thereâs inflammation.
- Metabolic panels test liver and kidney function.
- Vitamin D, B12, and folate tests look for vitamin deficiencies.
- Iron and ferritin tests look for iron deficiency.
- Swallowing a small camera can show problems in your digestive tract.
- Imaging tests show signs in the intestine, like wall thickening or changes to blood vessels.
- Genetic testing looks for human leukocyte antigens to rule out celiac disease.
If you’re on a gluten-free diet, you’ll need to come off it before having the antibody test so the results will be correct.
If blood and other tests show that you might have celiac disease, youâll probably need to have an endoscopy. This procedure lets your doctor look at your small intestine and take a bit of tissue to see whether itâs damaged.
If you have a rash, doctors will take a small sample of your skin to look for signs itâs caused by celiac disease. This rash is easy to confuse with other skin problems.
Also Check: Does Dunkin Donuts Have Gluten Free Donuts
Diagnosing Gluten Sensitivity / Gluten Intolerance
It is important to distinguish between celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, also known as gluten intolerance, in order to ensure you get the right care. Your doctor can test for celiac disease with a simple blood test. If your test results for celiac disease are negative but you still have symptoms, you may then be diagnosed with non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Learn more about getting tested for celiac disease.
An important note on getting tested: you must continue to eat gluten. Going gluten-free before getting tested can affect your results. If youre already gluten-free but want to get tested, consider undergoing a gluten challenge.
Complete our celiac disease symptoms checklist and then share the results with your doctor to get the conversation about getting testing started.
Who Should Be Tested For Celiac Disease And How Often
Read Also: Is Chipotle Rice Gluten Free
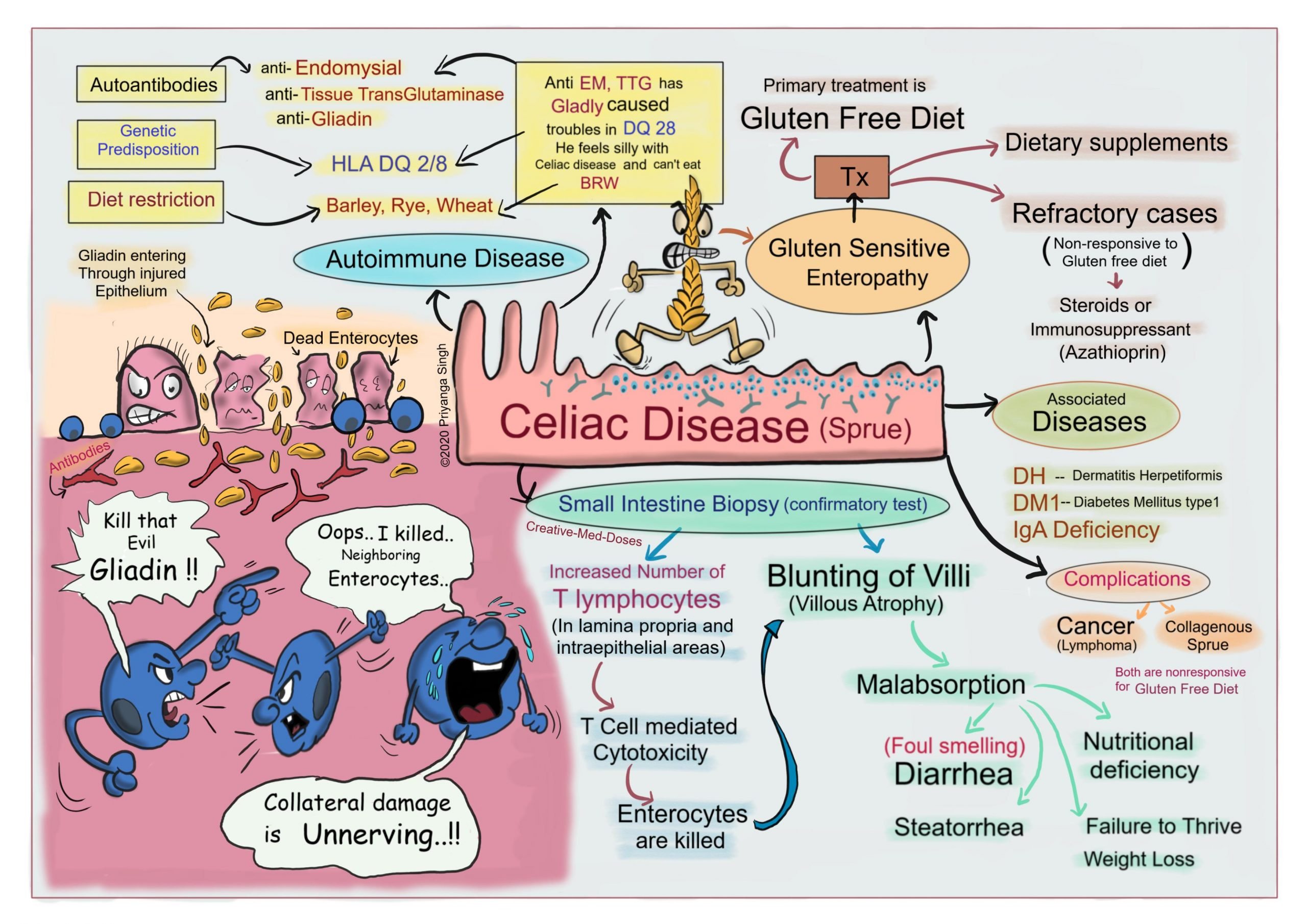
How Is Celiac Disease Treated
The only way to treat celiac disease is to permanently remove gluten from your diet. This allows the intestinal villi to heal and to begin absorbing nutrients properly. Your doctor will teach you how to avoid gluten while following a nutritious and healthy diet. They will also give you instructions on how to read food and product labels so you can identify any ingredients that contain gluten.
Symptoms can improve within days of removing gluten from the diet. However, you shouldnt stop eating gluten until a diagnosis is made. Removing gluten prematurely may interfere with test results and lead to an inaccurate diagnosis.
What Exactly Is Celiac Disease
Much has been said lately about celiac disease and gluten sensitivities. While gluten-free diets have become somewhat trendy, celiac disease is a very real disorder that has the potential to significantly impact quality of life if it is not properly managed.
Celiac disease is a hereditary autoimmune condition that can develop in genetically predisposed individuals during childhood or adulthood. People with celiac disease experience small intestine damage as a result of eating gluten, which is a specific type of protein that is found in wheat, barley and rye. When gluten is ingested, it triggers an immune response that attacks the villi, which are small, threadlike projections that line the surface of the small intestine and facilitate nutrient absorption. Having damaged villi means the body cannot properly process and benefit from important nutrients.
You May Like: What Foods Are Naturally Gluten Free
Complications Of Celiac Disease
Missed or late diagnosis together with prolonged consumption of gluten-containing foods in celiacs can lead to various complications:
- tumors and intestinal pathologies: risk of developing neoplasms such as intestinal carcinoma and non-HodgKing lymphoma, or ulcerative jejunum-ileitis increases with advancing age, which determines the appearance of ulcers on the bowel wall
- diseases affecting central and peripheral nervous system, cardiovascular system, endocrine system, liver, skin
- atrophy of the spleen and reduction of its functioning with a greater predisposition to contract infections
- lactose intolerance, which usually resolves a few months after starting the gluten free diet
- persistence of symptoms: in less than 1% of cases the symptoms and inflammation do not resolve even after eliminating gluten from one’s diet with the occurrence, for example, of collagenosic sprue .
Celiac Disease And Dental Problems
Celiac disease spares no part of the human body. One area that can get affected is the mouth. Dental enamel defects and frequent oral ulcers can occur in celiac disease.
Enamel is the outer lining of the teeth. Dental enamel defects that develop in celiac disease, and the number of teeth affected, are strongly associated with the time of onset of the symptoms. The defects most commonly occur in the permanent teeth, usually developing before 7 years of age when the permanent teeth are in development. The enamel defects tend to occur symmetrically in all four sections of teeth in the mouth. Various grades of enamel defects can be seen including pitting, grooving or complete loss of enamel.
Some patients with celiac disease can have delayed eruption of teeth. Recurrent aphthous ulcers in the mouth is another manifestation of celiac disease. In some patients, this could be the only symptom of celiac disease. Sometimes, this is due to an autoimmune phenomenon. They do tend to improve with gluten-free diet.
Also Check: Is Coconut Flour Gluten Free
Diagnosing Celiac Disease & Gluten Sensitivity In Adults
NYU Langone gastroenterologistsdoctors that specialize in diseases of the digestive systemare experts in diagnosing celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the digestive tract after a person consumes gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, barley, and other foods and beverages. Some vitamins, medications, and personal care products such as lip balm contain gluten.
During digestion, food passes through the intestines, where nutrients are absorbed into the body. Most of this absorption occurs in the small intestine, where tiny finger-like projections along the small intestinal lining, called villi, sweep the nutrients from food into the bloodstream.
People with celiac disease, however, have a genetic susceptibility to recognize gluten differently. When someone with celiac disease eats food that contains gluten, it triggers the immune system to attack the small intestine. The body forms antibodies, or proteins, that attempt to remove gluten from the body as if it were a foreign invader. The antibodies also attack the lining of the small intestine, causing inflammation.
Over time, recurrent inflammation damages the villi in the small intestine, and the body doesnt absorb nutrients very well. This can lead to malnutrition and unwanted weight loss. The chronic inflammation also can cause abdominal discomfort.
When To See A Healthcare Provider/go To The Hospital
See your healthcare provider if you or your child has had diarrhea or digestive discomfort for two weeks or more. You should see your healthcare provider before you try a gluten-free diet as that can change the test results.
All first-degree family members of people diagnosed with celiac disease should be tested, as their risks increase to a 1 in 10 chance, even for those with no symptoms.
Celiac disease can masquerade as many, many other conditions. However, having some of these symptoms doesn’t mean you necessarily have celiac diseaseit just means you should consider being tested for the condition.
Also Check: Gluten Free Frozen Dough Balls
How Is Gluten Intolerance Treated
Theres no cure for gluten intolerance. But most people find relief from symptoms by following a gluten-free diet. You should work with your healthcare provider and a dietitian to plan your diet.
You can also ask your healthcare provider about adding probiotics to your diet. Probiotics help increase the good bacteria in your gut. They may reduce symptoms of bloating, gas or constipation.
Some research suggests that taking certain enzymes may help you digest gluten. But experts are still investigating this treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider before taking any enzymes.
What Are The Symptoms Of Coeliac Disease
The symptoms of coeliac disease can range from severe to minor or atypical, and may even go undetected. Some symptoms can be wrongly confused with irritable bowel syndrome or a sensitivity to wheat or other food, while other symptoms may be put down to stress or getting older.
The most common symptoms of coeliac disease in adults include:
- irritability.
Don’t Miss: Where To Buy Gluten Free Empanada Dough
