Myth Vs Fact: Celiac Disease Vs Wheat Allergy
MYTH: Celiac disease is the same thing as a wheat allergy.
FACT: Celiac disease is not the same as a wheat allergy.
Although celiac disease may appear to be similar to a wheat allergy because of the need to avoid certain foods, these two conditions are entirely different, with different health effects and treatments.
Wheat contains a protein called gluten which is also in other foods, including rye and barley. Importantly, not all gluten-free foods are wheat-free. And not all wheat-free foods are gluten-free.
The term gluten-allergy can be confusing. Some people use this term to mean celiac disease, and some use this term to mean wheat allergy, and others use this term if they choose to avoid gluten for other reasons such as intolerance or preference. Clear communication about the type of reaction to wheat or gluten can inform the type of avoidance and treatment required. If you are not sure about the type of reaction you may have, please ask your doctor.
Wheat allergy is one of the most common food allergies in Canada. A food allergy is your bodys immune system overreacting to a specific protein in a food, such as wheat, milk, or peanut. Consuming food you are allergic to can trigger a reaction involving different symptoms, from itching, redness, and hives, to wheezing, inability to breathe, and loss of consciousness. A severe allergic reaction can even be fatal. People allergic to wheat are allergic to a part of wheat, which is not always the gluten part.
Diagnosis Of Gluten Sensitivity
There is no validated test to diagnose GS. Some online labs offer blood, saliva, or stool tests for gluten sensitivity, but they are invalidated and not recommended.
It is impossible to develop a test when the mechanism of gluten sensitivity has not been determined. Diagnosis is made by ruling out CD and wheat allergy while the patient is on a gluten-containing diet. Once both are ruled out, a gluten elimination diet is prescribed. If symptoms improve, the patient is deemed to have gluten sensitivity. Using a response to initiation of a gluten-free diet as a prognostic indicator will give inaccurate results, as both celiac and GS can have similar responses to a gluten-free diet.
How Do You Know What You Have
If you experience negative symptoms after eating gluten-containing foods, it is a pretty safe bet that you have some kind of disease, allergy, or sensitivity to gluten. Unfortunately, identifying the exact condition you have may not be quite so simple. The first step in diagnosing your problem is to have your doctor run a blood test which may be followed by other diagnostic tests. While running these tests, you need to continue consuming gluten-containing foods it is only after you have a diagnosis that you should switch to a gluten free diet.
A blood test cannot confirm a diagnosis of celiac disease, but it can reveal the presence of immunoglobulin E antibodies which would suggest some kind of autoimmune or allergic reaction to gluten. If your blood test comes back positive for IgE antibodies, your doctor may recommend an endoscopy to check the small intestine for damage damage to the lining of the small intestine would confirm a diagnosis of celiac disease while a lack of damage would suggest wheat allergy, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, or gluten intolerance. To confirm a wheat allergy, your doctor may want to perform a RAST or skin prick test.
Don’t Miss: Jason’s Deli Chocolate Mousse Recipe
Celiac Disease Diet Market 2021 Key Report Highlights Segments Geographical Outlook Competition Dynamics And Growth Objectives By 2027your Browser Indicates If You’ve Visited This Link
Brandessence Market Research is working on a new report title ” CeliacDisease diet Market: Global Size, Trends, Competitive, Historical & Forecast Analysis, 2018-2024. Increasing prevalence of celiacdiseases& gluten allergies and growing awareness among people are key drivers for Global CeliacDisease Diet Market.
Chip Design
Prevalence Of Other Diseases

Research indicates that 25 percent of patients with autoimmune diseases have a tendency to develop additional autoimmune diseases.
Because celiac disease is an autoimmune disease, people with celiac disease may have a higher risk of collecting additional autoimmune diseases than someone with gluten sensitivity.
However, its important to note that many researchers say gluten sensitivity is a precursor to autoimmune disease, and Dr. OBryan makes a clear argument for this in his groundbreaking book. This means both disorders, if left unmanaged, put you at higher risk for accumulating additional autoimmune diseases.
Read Also: Is Kraft Zesty Italian Dressing Gluten Free
Similar Symptoms Different Severity
Two people can have the same symptoms after eating gluten bloating, stomach pain, diarrhea but have two different gastrointestinal diseases: Celiac disease and gluten intolerance, or non-celiac gluten sensitivity .
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder, whereas gluten intolerance is a sensitivity, says Northwestern Memorial Hospital Clinical Dietitian Bethany Doerfler, MS, RD, LDN. NCGS does not typically have a full negative impact on overall health like celiac disease can.
Both celiac disease and NCGS are treated by not eating gluten. Someone with celiac disease must avoid gluten completely for their entire life, while someone with NCGS may see symptom improvement by simply reducing gluten and carbohydrate intake.
Removing gluten from your diet if you dont have celiac or a gluten intolerance will give you no health advances, Doerfler adds.
What Happens When Someone With Gluten Intolerance Or Sensitivity Eats Gluten
While someone with either an intolerance or a sensitivity to gluten will not experience an immune response to the same degree someone with celiac disease would, they will experience some GI issues due to the mal-absorption of the protein.
“We think of gluten intolerance as a fairly tolerable illness, though, if we are unable to fully metabolize and digest the micronutrients, this becomes an issue of vitamin and mineral deficiencies as well as fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies as a consequence of a diuretic effect on the digestive system,” says Mancella.
In other words, gluten may inhibit the absorption of other vitamins and minerals in those with a sensitivity or intolerance.
In short, someone with celiac disease will oftentimes experience much more adverse reactions than someone with gluten intolerance or sensitivity. However, neither group should be consuming gluten. When in doubt, get testedâyou can never be too cautious when it comes to your health.
You May Like: Are Ezekiel English Muffins Gluten Free
Someone Must Be Eating Gluten For Tests To Be Accurate
Basic screening for celiac disease includes a serum TTG IgA and total serum IgA. Total serum IgA needs to be done to rule out IgA deficiency which occurs in about 10% of celiac patients. If IgA deficiency is present, the TTG IgG must be used but is less accurate. Further testing may be needed in those situations.
Some labs include a DGP-IGA and EMA in their celiac screen/panel or do these tests as a reflex. The confirmatory test is an endoscopic biopsy. The biopsy is indicated if tests are positive and are required for diagnosis.
Of note, many celiac centers and practitioners follow a more extensive evaluation process involving screening antibodies, genetic testing, clinical response to a gluten-free diet, and endoscopy. These protocols and other testing algorithms are beyond the scope of this article.
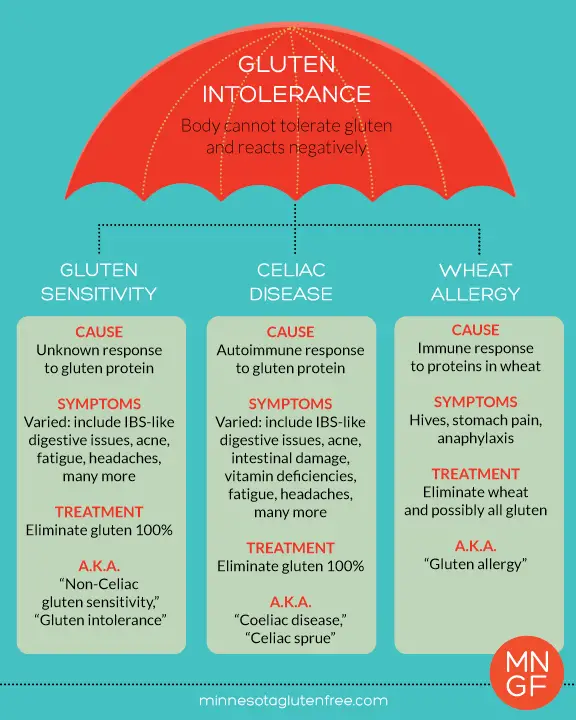
Celiac Disease Vs Gluten Sensitivity Vs Wheat Allergy
To help pinpoint what might be ailing you, it helps to understand the basics of three common gluten and wheat-related health conditions, as well as the differences between them.
Celiac disease is a chronic immune-mediated disorder. If you have CD, ingesting gluten damages the lining of the small intestine, making it difficult to absorb necessary nutrients. The condition is genetic, and experts believe it affects around one in every 150 people, although it may be underdiagnosed, since many people with CD may not even be aware that they have it.
Some people with a mild form of the disease may not experience any symptoms. Most however, will develop common signs like diarrhea, constipation, gas, bloating, abdominal pain, fatigue and sometimes nausea or vomiting. Some people with celiac disease may not have digestive issues but develop other symptoms, such as bone or joint pain, depression or anxiety, headaches, mouth problems, like canker sores or dry mouth, a smooth, shiny tongue and tingling or numbness in their hands and feet. Reactions typically arent immediate and symptoms may appear several hours after eating gluten. Left untreated, CD can lead to malnutrition, dermatitis herpetiformis , infertility, anemia, osteoporosis and a higher risk of some cancers, among other health problems.
Wheat allergy is like other food allergies, in which your bodys immune system overreacts to a substance most people find harmless in this case, wheat.
Don’t Miss: Jason’s Deli Gluten Free
Three Factors Must Be Present To Have Active Celiac Disease
1. Gene.
Forty percent of the population carries one of the at-risk genes for celiac disease. Of that 40%, only 5% have active celiac disease. The reason for this is being investigated. Patients must carry either the HLA-DQ2 or the HLA-DQ8 gene to be at risk for celiac disease. You are at risk if you have either. You do not need both to be at risk. But, the presence of these genes is not diagnostic. The presence of either DQ-2 or DQ-8 only indicates a predisposition. If neither marker is present, celiac disease can be ruled out. Researchers are currently evaluating other genes for their involvement in celiac disease. Of note, there are currently no scientifically validated genes associated with NCGS.
2.Gluten.
Patients must be consuming gluten for CD to be active.
3.Environmental trigger.
Not all triggers are known, but identified triggers include early/repeated infections, pregnancy, and GI infections, antibiotic use at an early age.
What A Doctor Can Do
If youre experiencing unusual symptoms and believe you might have CD, GS, a wheat allergy or another digestive condition, reach out to your healthcare provider . Your doctor can help pinpoint what ails you, refer you to the appropriate specialists and begin treatment to alleviate your symptoms. Avoid self-diagnosing your condition or eliminating gluten from your diet before your appointment, which could influence your test results, leading to a misdiagnosis and slower recovery.
And if your tests results reveal that you do not have a digestive issue related to wheat or gluten intake but youre still cutting them out of your diet to slim down or for some other perceived health benefit, you may want to reconsider. While some people may find it impels them to choose healthier foods in general, theres no real evidence that eliminating gluten will help you drop pounds or improve your overall wellbeing. Whats more, if youre not careful, eliminating gluten could deprive you of valuable nutrients especially fiber, but also iron and calcium. Many gluten-free foods are also loaded with added sugar, too much of which is unhealthy in itself.
In the end, the gluten decision is best left to you and your doctor and with a little knowledge, you can make the right choice for your health.
This content originally appeared on Sharecare.com.
You May Like: Gluten Free Bread Crumb Substitute
Summary Of The Difference Between Celiac Disease And Gluten Sensitivity
Celiac Disease Vs Gluten Intolerance: Spotting The Difference
Gluten free diets have risen in popularity, but there are many people who do not understand what being gluten free entails, or why someone would need to be gluten free. Celiac disease and gluten intolerance are both conditions that relate to gluten. While they might have some similarities in their symptoms, there are distinct differences between both conditions. Heres what you should know about celiac disease versus gluten intolerance.
You May Like: Gluten Free Cookies And Cream Ice Cream
Celiac Vs Gluten Intolerance: Is There A Difference Between Celiac Disease And Gluten Intolerance
Celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and wheat allergy are all conditions that are all affected by gluten. While similar in their condition, there are distinct differences in each and how to treat them. Read on to learn more about their differences.
In recent years, the gluten free diet has gained a great deal of traction, but many people still dont have a true understanding of what it means to go gluten free or the exact why someone would need to.
Gluten is a type of protein found in certain grains including wheat, barley, and rye it plays a role in binding grain-based ingredients together in recipes, and it gives bread its spongy texture. The truth is that the gluten free diet is not designed for weight loss, as many tend to believe. It is much more beneficial when used as a strict, long-term eating plan for people with celiac disease, gluten intolerance, gluten sensitivity, or wheat allergy.
In this article, well explore the difference between each of these specific conditions as well as their symptoms. Well also take a quick look at how these conditions compare and what it really takes to follow a gluten free diet.
Celiac Disease Vs Gluten Sensitivity
Gluten refers to a family of proteins found in grains like wheat, rye, and barley. Celiac disease is an immune response against these proteins that involves damage to the lining of the small intestine. The disease can be confirmed by a blood test and upper endoscopy.
“Gluten sensitivity is less well-defined,” says Dr. Shirley Paski. “There may be symptoms that correlate with gluten exposure, but no measurable immune response or intestinal damage.”
Symptoms for celiac disease and gluten sensitivity can be similar and include:
- Diarrhea
- Bloating
- Itchy skin
Celiac disease can also cause migraines, itchy blisters, and fatigue. If celiac disease is ruled out, your doctor or dietician may recommend an elimination diet trial, which can reveal gluten sensitivity.
Don’t Miss: Gluten Free Pizza Crust Publix
