What Is It And What Is It Used For
The Gluten Sensitivity Test determines the presence of gluten sensitivity markers, in particular:
- IgA or IgG Anti-Transglutaminase to exclude a possible celiac diagnosis
- IgA and IgG Anti-Gliadin confirm possible gluten sensitivity
This is one of the first tests able to evaluate non-celiac gluten sensitivity, a disorder affecting people who suffer from intestinal and general disorders due to gluten intake, but who do not have celiac disease and are not allergic to wheat.
Gluten sensitivity often occurs in people who suffer from an irritable colon and intestinal inflammation, because it is easier for food that has not been completely digested to come into contact with the immune barrier and trigger off an inflammatory response.
The Best Test For Gluten Intolerance
I believe that people are becoming increasingly aware that gluten is not the best food ingredient for us it can be very difficult to digest, and can promote significant inflammation both in the gut and in the body as a whole, resulting in chronic pain, fatigue, brain fog, skin irritation, mood imbalances and more. There are a variety of labs that offer testing for gluten intolerance- in fact, all the big commercial labs offer the tests. I have found, however, that sometimes those blood tests are not as sensitive as some others. In my view, the best test for gluten intolerance is a stool test offered by a lab called Enterolab.
The markers that are tested for gluten intolerance are anti-gliadin antibodies and anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies. Both are looking for auto-immune reactions in the body that are caused by the ingestion of gluten. These are the markers that are assessed in blood testing too.
Enterolab uses a stool sample to look for those markers. I have found this to be a more sensitive test than standard blood tests . In several of those cases, the bloodwork showed negative where the stool results showed positive. Can we rule out false positives 100%? No, we cant, but I can say that the results were reflective of the health issues of those patients, and all those patients felt better when adopting a gluten-free diet.
Do You Need Help With Your Health
We have the tools to discover why you may be having trouble with a weakened immune system. Its not difficult as long as youre ready to make some dietary and lifestyle changes. If that sounds daunting, dont worry. We will hold your hand through the changes and make each step of change an easy one.
Contact us for a Consultation Call
Don’t Miss: Is Nature Valley Granola Gluten Free
Current Celiac Lab Tests Are Known To Be Insensitive To An Early Diagnosis
There is much research that already states this problem with those particular blood tests. Those of us who follow this closely KNOW that these tests are not terribly sensitive. We know that severe damage to the small intestine needs to occur before these tests show positive, in the main.
Why am I upset with this research? Because their conclusion is terribly misleading. Doctors that dont take the time to read the entire paper, and I promise you that will be many, will come away with false information and their patients will suffer as a result. It is no wonder doctors are confused!
In my opinion, a test for celiac disease cannot be termed highly sensitive and specific if it misses when partial damage to the small intestine has occurred. The risks associated with celiac are too severe to only use tests that are accurate when the small intestine is all but destroyed. They also state: The prevalence of the celiac disease in primary care patients presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms is 2% to 4%.
However, gastrointestinal symptoms in primary care are common, and screening all patients for celiac disease is neither necessary nor efficient. Wow, unnecessary for whom? Inefficient for whom?
How To Diagnose Gluten
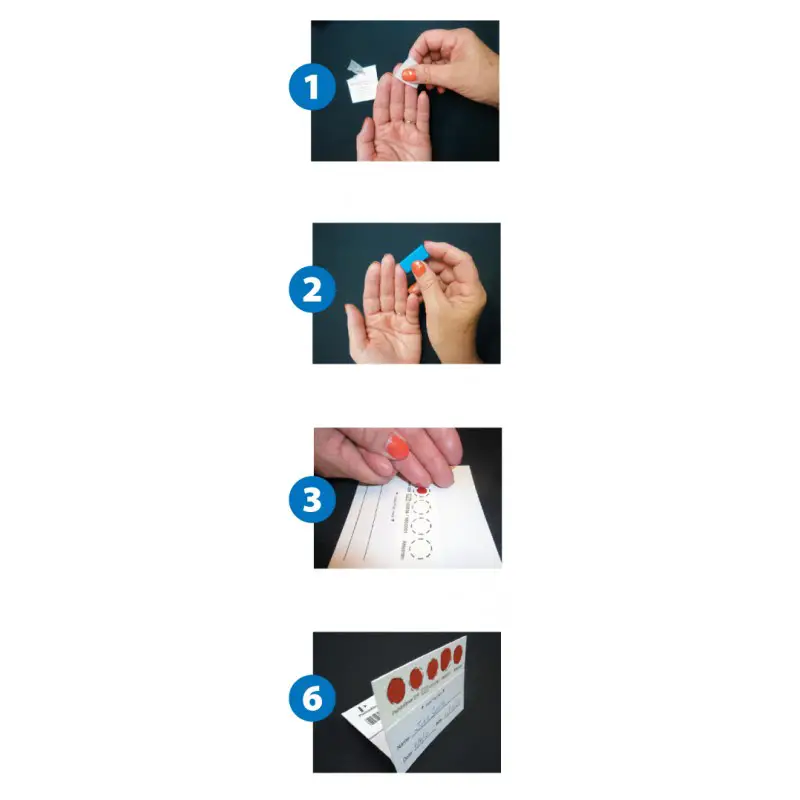

Medicovers latest, innovative laboratory package offers a specialized, fast and effective test for gluten-dependent diseases and digestive problems through a single blood sample. The package includes tests for celiac disease/gluten sensitivity, food allergy to gluten-containing grains and non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
These laboratory tests should be performed before starting a gluten-free diet, as the diet may result in the disappearance of antibodies and false-negative tests.
Read Also: Whole Foods Gluten Free Pie
Symptoms Of Celiac Disease
Although digestive issues are common in children with celiac disease, most adults do not experience these symptoms. Instead, the following signs are often a red flag for celiac disease in adults:
- Liver and biliary tract disorders
- Osteoporosis or osteopenia
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Seizures or migraines
- Unexplained iron-deficiency anemia
Whether or not you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to undergo celiac disease testing if you have a first-degree relative with the condition, as this puts you at a one in ten risk of developing celiac yourself.
However, if you suspect that you have gluten intolerance rather than celiac, the single best way gluten intolerance test is to remove it from your diet, note how you feel without it, and how you feel when you add it back in.
Labs And Tests For Gluten Sensitivity
Celiac disease must be ruled out before gluten sensitivity can be diagnosed. Doctors usually start with a panel of celiac blood tests. These tests look for certain antibodies. There is some evidence that two of those tests could also find non-celiac gluten sensitivity:
Read Also: Where To Order Gluten Free Pizza
Genetic Celiac Disease Test
Genetic testing a simple swab of the cheek can tell you if you carry the genes for celiac disease . If you do not carry the genes it is impossible for you to ever develop the disease. Upon that point, everyone is in agreement. However, beyond that, there are some varying opinions. Many doctors point out that if you arent showing signs of the disease theres no reason to implement a gluten-free diet. Personally I think having one gene, let alone two is more than enough reason to embark on a gluten-free diet if you are experiencing any health issues. Of course, following up on a positive genetic test with available blood tests for both celiac disease and gluten sensitivity, along with the presence of typical symptoms and the improvement of said symptoms once a gluten-free diet is embarked on, all total to a valid diagnosis, without the need of an intestinal biopsy.
Anti-Reticulin Antibodies, IgA, abbreviated ARA-IgA. This test is not ordered as frequently due to its lack of sensitivity and specificity as compared to other autoantibodies. It is found in about 60% of celiac disease patients and about 25% of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis, the skin condition associated with celiac disease. When used, ARA is ordered along with other celiac disease tests as part of a panel.
Who Should Take The Test Of Gluten Sensitivity
It is estimated that 6-8% of the population are gluten sensitive, and it is a chronic condition that is shown with intestinal or general symptoms of varying intensity, related to an intake of gluten.
This sensitivity is generally associated with the appearance of anti-gliadin antibodies , a molecule present in gluten, a protein compound found in wheat, spelt, rye, kamut®, barley and other cereals.
Unlike celiac disease, where ingesting gluten damages the intestinal mucous until the villi atrophies, leading to poor absorption, the symptoms of gluten sensitivity are more obvious from bad reactions to food, the so-called delayed allergies, or better known as but improperly called food intolerances.
You should take the test if you have one or more of these symptoms when you eat food containing gluten:
- Chronic fatigue, difficulty in concentrating and sleeping
- Digestive difficulty, bloated stomach, sense of nausea, stomach pain and cramps
- Gastric hyperacidity, gastritis
- Diarrhoea, constipation, irregular bowel movements.
- Flatulence, aerophagy.
- Cramp, muscular tremors, weak muscles, joint and muscle pain.
Read Also: Gluten Free Egg Free Breakfast
When To Speak With A Doctor
Home tests may indicate whether a person has celiac disease, but anyone with symptoms of gluten intolerance should consider speaking with a doctor for a diagnosis.
No effective gluten sensitivity blood or stool tests exist. Doctors diagnose it by ruling out other conditions and encouraging the person to try an elimination diet.
Below are the answers to some commonly asked questions about gluten intolerance testing.
How To Test For Gluten Intolerance And Celiac Disease
Science Based Amy Myers, MD
Amy Myers, M.D. is a functional medicine physician, trained and certified by The Institute of Functional Medicine. Dr. Myers earned her Doctor of Medicine at the LSU Health Science Center, and completed her Emergency Medicine residency at the University of Maryland Medical Center.
Dr. Myers retired from her functional medicine clinic, Austin UltraHealth, where she served thousands of patients, to empower those who were failed by conventional medicine. Shes a 2x New York Times bestselling author, and the founder and CEO of the health & lifestyle e-commerce brand, Amy Myers MD®.
Do you experience bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, or headaches after eating bread and other products containing wheat, barley, or rye? You could have a gluten intolerance, also known as non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Fortunately, gluten intolerance testing can help you pinpoint the problem.
Recommended Reading: King Arthur Gluten Free Pancakes
Are There Other Ways To Test For Celiac Disease
Genetic tests that look for the markers that are strongly associated with celiac disease have recently become available. These tests look for the Human Leukocyte Antigen markers DQ2 and DQ8. A positive result does not diagnose celiac disease since about 30% of the general population also carry these markers but do not have the disease. However, almost all people with celiac disease are positive for DQ2 or DQ8, so a negative result can essentially rule out celiac disease in those individuals for whom results of other tests, including biopsy, are unclear. These tests are most useful for family members of individuals with the disease that fall into a high-risk category and for those with other diagnostic test results that are inconclusive.
What Is Being Tested
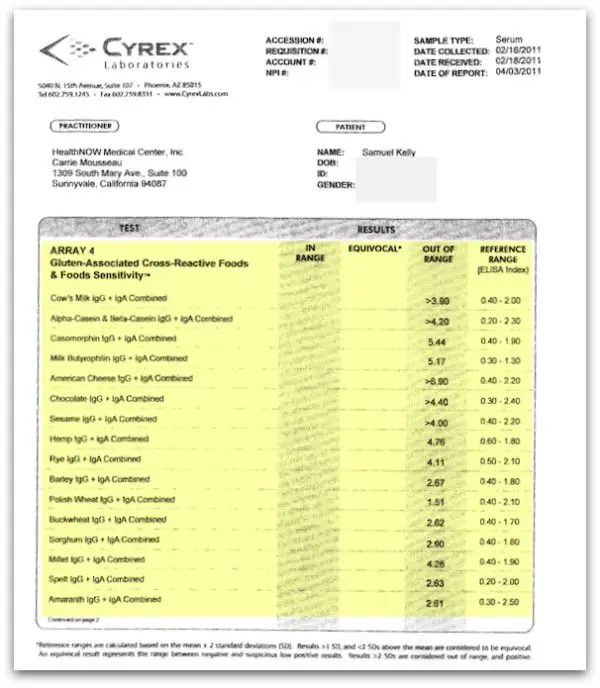
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by an inappropriate immune response to gluten, a protein found in wheat, and related dietary proteins in rye and barley. Celiac disease antibody tests help diagnose and monitor the disease and a few other gluten-sensitive conditions. These tests detect autoantibodies in the blood that the body produces as part of the immune response.
This immune response leads to inflammation of the small intestine and to damage and destruction of the villi that line the intestinal wall. The villi are projections, small tissue folds that increase the surface area of the intestine and allow nutrients, vitamins, minerals, fluids, and electrolytes to be absorbed into the body. When a susceptible person is exposed to gluten, the persons body produces autoantibodies that act against constituents of the intestinal villi. When villi are damaged or destroyed, the body is much less capable of absorbing food and begins to develop signs and symptoms associated with malnutrition and malabsorption.
A tissue biopsy of the small intestine is still considered the gold standard to use to confirm a diagnosis of celiac disease, but the availability of less invasive blood tests to screen for celiac disease has reduced the number of biopsies needed.
You May Like: Where To Buy Gluten Free Lasagna Noodles
Who Should Get Screened
Blood And Genetic Tests
To find out if you have celiac disease, you may first get:
Blood test. This test checks for certain antibodies in your blood. Almost everyone with celiac has them in their blood at higher-than-normal levels.
HLA genetic test. This looks for the HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 genes. If you donât have them, itâs very unlikely that you have celiac disease. You may get a blood test, saliva test, or a swab of the inside of your cheek.
These tests arenât enough to show that you have celiac disease. But if the results show that you might, or it seems very likely you might have celiac disease, your next step is endoscopy.
Recommended Reading: Thousand Island Dressing Gluten Free
Search For The Nearest Any Lab Test Now Locationwhere This Test Is Available
We use cookies to enhance your visitor experience and our ability to customize content to fit our customer’s needs. Learn more about our cookie policy and which ones we use or you may switch them off in settings.
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognizing you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
These cookies are required to move around a website and use its features, such as browsing as a registered visitor, or making a purchase. Our website uses strictly necessary cookies. You may be able to block these cookies through your browser settings, but some parts of the websites may not function properly. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable information.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
So How Do I Get Diagnosed
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity is diagnosed by process of exclusion. Experts recommend that you first get tested for a wheat allergy and for celiac disease. If both of those are negative, then your doctor may recommend a gluten elimination diet. If symptoms improve on a gluten-free diet, then you likely have non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
It is very important that a knowledgeable physician oversee this entire process, which can help to omit patients self-diagnosing themselves and to reduce the likelihood of a placebo effect occurring during dietary intervention.
Im already gluten-free and I feel much better than I did when eating gluten. Can I just assume that I have non-celiac gluten sensitivity?
It is possible that you have celiac disease and not non-celiac gluten sensitivity. But because celiac disease is a lifelong condition requiring strict adherence to a gluten-free diet and proper management by a knowledgeable physician, it is important that an accurate diagnosis is made. Additionally, if you have celiac disease, it is important to confirm the diagnosis, as your family members could be at risk for the disease and may not know it.
Are there any dangers to a false diagnosis of non-celiac gluten sensitivity?
Read Also: Gluten Free Meats And Cheeses
In What Cases Is This Laboratory Package Recommended
In all cases where we experience symptoms associated with gluten-dependent diseases, a thorough medical examination as soon as possible is important. Self-diagnosis and a wrong choice of diet can even cause serious damage to our body, so a full laboratory test is recommended even for mild symptoms.
If there has already been celiac disease in the family, prevention should be a priority due to genetic accumulation. The most important thing is to make sure that the necessary diagnostics are carried out, in which Medicovers latest laboratory test package, compiled specifically for the diagnosis of gluten-dependent diseases, offers help.
Gluten Intolerance Testing At Home
I have found the single best way to determine if you have an issue with gluten is with an elimination diet. This means you remove gluten from your diet for at least 30 days and then reintroduce it. Please note that gluten is a very large protein. It can take months or even years to completely clear from your system. The longer you can eliminate it from your diet before reintroducing it, the better.
Heres the simple advice that I shared with all the patients in my clinic: If you feel significantly better when youre not eating gluten and worse when you reintroduce it, then gluten is likely a problem for you. Remember, to get accurate results from this testing method you must eliminate 100% of the gluten from your diet.
Don’t Miss: Gluten Free And Dairy Free Ice Cream
Can I Have Oats In My Diet
This is somewhat controversial. Some experts feel that oats should be avoided by those with celiac disease while others believe that most people can tolerate small amounts. They feel that the proteins found in oats are not contributing significantly to celiac disease. This is something you should discuss with your health care practitioner and a nutritionist.
Diagnostic Tests For Celiac Disease

If you experience digestive symptoms or signs of poor vitamin and nutrient absorption, such as unexplained weight loss, an NYU Langone gastroenterologist can perform diagnostic tests to determine whether celiac disease may be the cause. For adults, doctors typically recommend both blood tests and biopsies, in which tissue samples are examined under a microscope, to confirm the diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: No Dairy No Gluten No Sugar
What Is Wheat Allergy
A wheat allergy is a type of food allergy that is usually mediated by an IgE antibody response to wheat. People who are allergic to wheat can experience itchy eyes or have difficulty breathing after dietary exposure. In this group of patients, unlike celiac disease, exposure to wheat doesnt cause long-term damage to the small intestine. Diagnosis of wheat allergy usually occurs through IgE antibody testing, but non-IgE-mediated wheat allergies can occur.
Diagnosis: What To Expect
Since celiac disease tends to run in families, if you have a parent, child, brother, or sister with the disease, talk to your doctor about whether you should be tested. Celiac disease is more common in people with type 1 diabetes, autoimmune liver disease, thyroid disease, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, or Williams syndrome. So if you have any of these conditions, you should also ask your doctor to test you for celiac.
Also Check: How Do I Know If I Have A Gluten Allergy